Canada Business Funding: Complete Guide to Financing a Canadian Business
Starting or expanding a small business in Canada?
Good news! There are tons of funding options available for Canadian entrepreneurs, whether you’re an existing business owner or thinking about starting a new venture.
Whether you’re looking for free money (and who isn’t?) or you’re open to self-funding a business, taking on a bit of debt, or selling a stake to investors, we’ve got the rundown on every possible way to get funding for your business in Canada.
This is the most comprehensive list of funding options for Canadian entrepreneurs (47 distinct types of funding – and counting!).
Ready to start funding your dream? Let’s go!

Four Categories of Small Business Funding
We’ve grouped the 47 types of funding for Canadian entrepreneurs into 4 broad categories:
- Self-Funding (using your own money)
- Free Funding (grants, subsidies & more)
- Debt Financing (loans and credit)
- Equity Financing (selling a stake to investors)
Within those four categories, there are dozens of types of funding. In the section below we give a quick breakdown of each type; then, in the rest of the guide, we go a bit deeper, with a quick description, pros & cons, and explanation and when you might want to use each type.
Here’s the complete list of 47 types of small business funding for Canadian businesses (I call this the “business funding universe” for Canadian entrepreneurs):
Canadian Business Funding Universe: 47 Distinct Types of Funding for Entrepreneurs
In the following sections I describe each of the four categories of funding, along with the types of funding in each category.
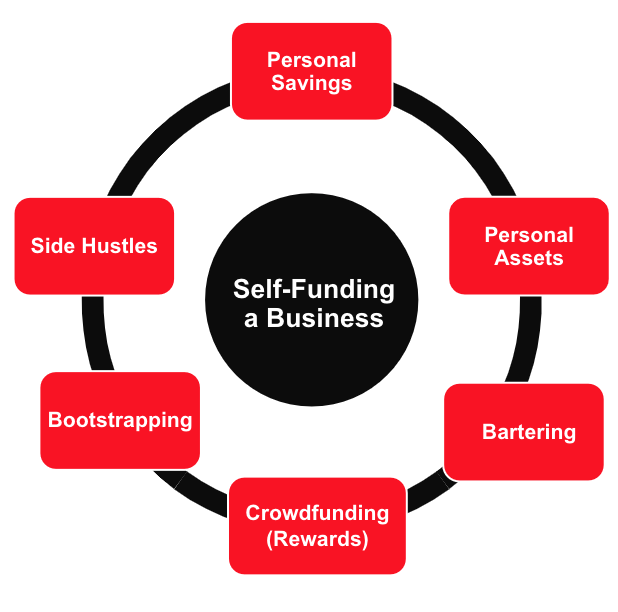
Self-Funding a Business in Canada

As the name suggests, self-funding is when you use your own finances, or revenue from early sales, to launch a business. It could be savings, selling assets, or maybe lottery winnings (?) fueling your entrepreneurial dream.
Here are the different types of self-funding that can be used for your business:
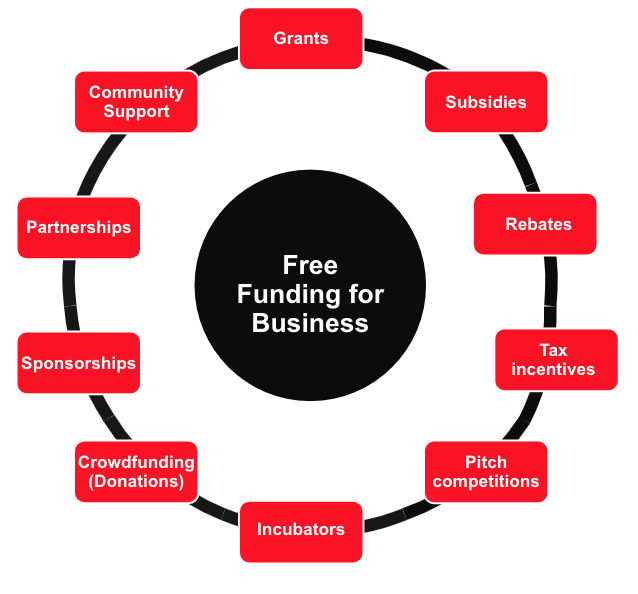
Free Funding for a Business in Canada
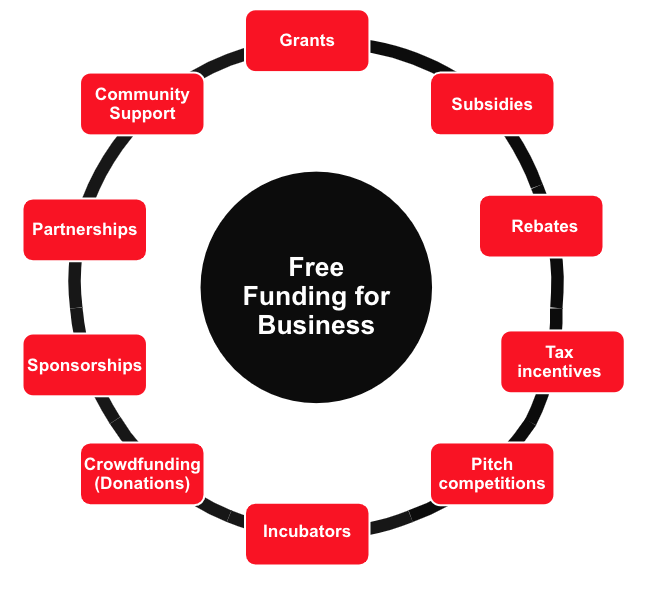
Yep, it’s not a fairy tale! Free money includes grants, subsidies, contests (and more) that you can snag without the obligation to repay.
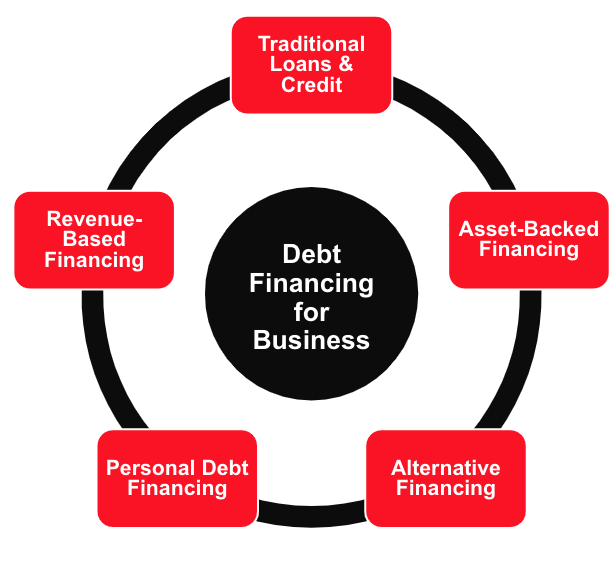
Debt Financing a Business in Canada

Just like a personal loan, debt financing involves borrowing money and paying it back over time with interest. You’ll find options like:
Traditional Loans & Credit

Traditional loans and credit for a Canadian business include many of the products that you’re probably familiar with:
Asset-Backed Financing

Asset-backed financing involves obtaining financing for your business that is backed by assets like equipment, inventory, and property. Here’s a quick description of each:
Revenue-Based Financing

Revenue-based financing is similar to asset-backed financing, but instead of securing the financing with assets, you’re securing it with an income stream (usually your business’s revenue). Here’s a quick description of the most common types of revenue-based financing in Canada:
Alternative Financing

Alternative financing for is a category that is growing in popularity for Canadian businesses (and I personally think crowdfunding is an area that has huge potential and will grow in coming years). Here are three of the most common types in Canada today:
Personal Financing

Using a personal loan, line of credit, or credit is a very common tactic among entrepreneurs to fund their business, whether it’s for a startup or to temporarily sustain a business during a dip in business:
Equity Financing for a Business in Canada
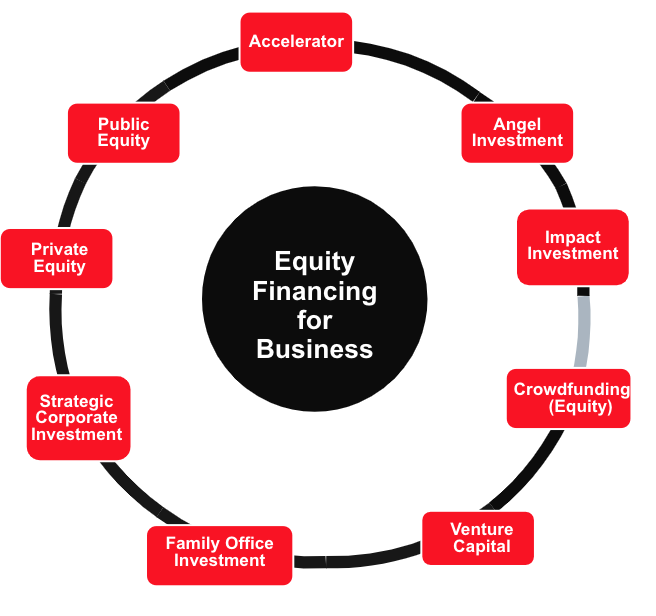
Think of equity financing as trading a piece of your company’s pie for cash. You’re offering up a slice of ownership in exchange for funding.
Here are the most common types of equity financing in Canada:
Self-Funding Your Canadian Business: 6 Strategies to Pay Your Own Way

When you’re starting out, your business is your baby, and you might decide to fund it yourself. This can mean tapping into your personal savings, considering the use of your retirement accounts, selling or leveraging personal assets, asking friends and family to chip in, or even starting a side hustle to drum up extra cash.
Personal Savings
Using your personal savings to fund your business is a straightforward approach. It’s like giving your business a loan from your own pocket. You won’t have to pay interest to a bank, but you’re taking on all the risk yourself.
Pros & Cons of Using Personal Savings for Your Business:
When to Use It: Use personal savings when you want to maintain complete control over your business and avoid debt, and when you have sufficient funds that won’t jeopardize your personal financial stability.
Personal Assets
Personal assets funding involves selling or leveraging valuable personal property, such as real estate, vehicles, or other significant possessions, to finance your business.
Pros & Cons of Using Personal Assets for Your Business:
When to Use It: Use personal assets when you need a large sum of capital quickly and are willing to risk or part with personal property to avoid taking on debt or outside investors.
Side Hustles
Side hustles involve doing additional jobs or freelance work alongside your primary business to earn extra income, which can be reinvested into your main venture.
Pros & Cons of Side Hustles (When Combined with Your Business):
When to Use It: Use side hustles when you need supplementary income to fund your business and can balance the additional workload without compromising the growth and management of your main business.
Explore Hundreds of Side Hustles on Our Business Ideas pageBartering
Bartering involves exchanging goods or services with another business or individual without the use of cash, allowing both parties to benefit from each other’s resources.
Pros & Cons of Using Bartering in Your Business:
When to Use It: Use bartering when you have valuable goods or services to offer and need to conserve cash while still acquiring necessary resources for your business.
Learn More About Bartering for BusinessCrowdfunding (Rewards)
Rewards crowdfunding involves raising small amounts of money from a large number of people through platforms like Kickstarter, offering backers non-monetary rewards such as products or services in return.
Pros & Cons of Using Rewards Crowdfunding for Your Business:
When to Use It: Use rewards crowdfunding when you have a marketable product or service and need to raise funds without taking on debt, while also seeking to build a loyal customer base and gain early market validation.
Learn More About Rewards Crowdfunding for BusinessBootstrapping
Bootstrapping involves funding your business through its own revenue streams without external financing. This can include selling products or services on social media, setting up an ecommerce website, and utilizing affiliate sales.
Pros & Cons of Bootstrapping Your Business:
When to Use It: Use bootstrapping when you prefer to retain full control and ownership of your business and have a viable product or service that can generate revenue from the start.
Learn More About Bootstrapping a BusinessFree Funding for Your Canadian Business: 10 Types of Free Money

To state the obvious: free money programs can offset your costs and help your business grow! And “free money” for businesses isn’t a myth – there are many programs and opportunities specifically designed to support small businesses in Canada.
Let’s get into those free money programs!
Grants
Grants are non-repayable funds provided by government agencies, private organizations, or non-profits to support specific business activities or projects, such as research and development, innovation, exporting, and many other business activities.
Pros & Cons of Business Grants:
When to Use It: Use grants when you have a project or initiative that aligns with the funding organization’s goals, and you can meet the eligibility requirements and commit to the application and reporting process.
Learn More About Grants to Start or Grow a BusinessSubsidies
Subsidies are financial assistance programs provided by the government to support specific business activities, such as wage support, employee training, export activities, or energy efficiency improvements.
Pros & Cons of Business Subsidies:
When to Use It: Use subsidies when you need to offset specific costs, such as wages, training, exporting, or implementing energy-efficient practices, and can comply with the associated regulations and reporting requirements.
Learn More About Business Subsidies in CanadaRebates
Rebates are partial refunds provided to businesses after the purchase of specific goods or services, often aimed at encouraging investment in particular areas, such as energy efficiency, technology adoption, or environmental sustainability.
Pros & Cons of Business Rebates:
When to Use It: Use rebates when making investments in areas eligible for rebate programs, such as energy-efficient equipment or environmentally friendly technologies, and when you can afford the initial expenditure and navigate the rebate application process.
Learn More About Business Rebates in CanadaTax Incentives
Tax incentives are financial benefits provided by the government to reduce a business’s tax liability. These include tax credits, which directly reduce the amount of taxes owed, and tax deductions, which reduce the taxable income on which taxes are calculated.
Pros & Cons of Business Tax Incentives:
When to Use It: Use tax incentives when you are undertaking eligible activities like research and development, capital investments, or environmentally sustainable projects, and can ensure proper documentation and compliance with tax regulations.
Learn About Business Tax Credits in CanadaPitch Competitions
Pitch competitions are events where entrepreneurs present their business ideas to a panel of judges, often comprising investors or industry experts, for a chance to win funding, mentorship, or other resources.
Pros & Cons of Pitch Competitions:
When to Use It: Use pitch competitions when you have a well-developed business idea or product and are looking for funding, exposure, or mentorship. They are particularly beneficial if you’re confident in your ability to present and defend your business concept in front of an audience and panel.
Learn More About Pitch CompetitionsIncubators
A business incubator is a program designed to support early-stage startups by providing resources such as office space, mentorship, networking opportunities, and sometimes funding, to help them grow and succeed.
Pros & Cons of Business Incubators:
When to Use It: Use a business incubator when you are an early-stage startup needing guidance, resources, and a supportive environment to develop your business idea, especially if you lack initial capital or industry connections.
Learn More About Business IncubatorsCrowdfunding (Donations)
Donations crowdfunding involves raising funds from a large number of people, typically via online platforms like GoFundMe, where backers contribute without expecting any financial return. This approach is often used for businesses with a strong community or social impact focus.
Pros & Cons of Donations Crowdfunding for Business:
When to Use It: Use donations crowdfunding when your business has a strong social or community aspect that resonates with potential donors, and when you’re able to create a compelling narrative to engage supporters. It’s particularly useful for early-stage businesses or projects that may not yet be attractive to traditional investors.
Learn More About Donations Crowdfunding for BusinessSponsorships
Sponsorships involve partnering with other businesses or organizations that provide financial or in-kind support in exchange for promotional opportunities, brand visibility, or other benefits.
Pros & Cons of Business Sponsorships:
When to Use It: Use sponsorships when your business can offer visibility or marketing benefits to sponsors, such as events, media coverage, or audience access, and when you’re looking for funding or resources without taking on debt or giving up equity. It’s particularly effective for businesses in industries like sports, entertainment, or community events.
Learn More About Business SponsorshipsPartnerships
Partnerships involve collaborating with other businesses or individuals to share resources, expertise, or market access for mutual benefit. These can take the form of formal joint ventures or informal collaborations.
Pros & Cons of Business Partnerships:
When to Use It: Use partnerships when your business can benefit from the complementary strengths of another entity, such as entering new markets, sharing costs for large projects, or enhancing your product or service offerings. It’s ideal when both parties have clearly defined roles and a shared vision for the partnership’s goals.
Learn More About Business PartnershipsCommunity Support (In-Kind)
In-kind community support involves receiving non-monetary assistance from local supporters, businesses, or organizations. This can include donated goods, services, volunteer time, or expertise.
Two organizations that provide significant in-kind support to businesses in Canada are Business Improvement Areas (BIAs) and Chambers of Commerce.
Pros & Cons of In-Kind Community Support for Business:
When to Use It: Use community support in-kind when you’re looking to reduce costs and build strong ties with the local community, especially for businesses with a community or social impact focus. It’s particularly useful for startups or small businesses that may not have the budget for certain resources or services.
Learn More About Business Improvements Areas (BIAs) and Chambers of CommerceDebt Financing for Your Canadian Business: 22 Types of Loans & Credit

When you’re looking for money to grow your business, debt financing can be a viable route. It’s all about borrowing funds and paying them back over time, usually with interest. Think of it as getting a loan that you’ll budget for and repay as your business earns.
We’ve identified 22 types of debt financing for Canadian businesses. To understand them better, we’ve grouped them into 5 sub-categories:
- Traditional Loans & Credit
- Asset-Backed Financing
- Revenue-Based Financing
- Alternative Financing
- Personal Financing
In the sections below we briefly cover each of the 5 sub-categories, along with the types of debt financing that fall into each:
Traditional Loans & Credit
When most business owners think of debt financing, this is often what they have in mind: the conventional loans and credit products offered by banks and credit unions.
We’ve identified 9 types of traditional loans and credit products for Canadian entrepreneurs, and cover each below:

Term Loan
A term loan is a lump sum of money borrowed from a lender that is repaid over a fixed period with regular payments, including interest. It’s typically used for significant investments like equipment purchases, expansion, or other capital expenditures.
Pros & Cons of Term Loans for Business:
When to Use It: Use a term loan when you need a large amount of capital for specific long-term investments and have a clear plan for generating the revenue needed to repay the loan. It’s suitable for established businesses with strong credit and predictable cash flow.
Learn More About Using Term Loans for BusinessGovernment-Guaranteed Loan
A government-guaranteed loan is a loan in which the government promises to repay a portion or the entirety of the loan if the borrower defaults. These loans are often provided through financial institutions and are designed to help businesses access funding with more favourable terms.
Pros & Cons of Government-Guaranteed Loans for Business:
When to Use It: Use a government-guaranteed loan when your business needs funding but may not qualify for traditional loans due to limited credit history or other factors. It’s ideal for businesses looking to expand, purchase equipment, or manage cash flow, especially in sectors that the government wants to support or stimulate.
Learn About Government Loans for Business in CanadaBridge Loan
A bridge loan is a short-term financing option designed to provide immediate cash flow to cover temporary needs or to “bridge” the gap until long-term financing is secured. These loans are often used for urgent business needs, such as paying for expenses during a financial shortfall or making a quick investment.
Pros & Cons of Bridge Loans for Business:
When to Use It: Use a bridge loan when you need immediate funds to cover short-term gaps or take advantage of time-sensitive opportunities, and you have a clear plan for repaying the loan quickly, such as securing a long-term loan or selling an asset.
Learn More About Using Bridge Loans for BusinessWorking Capital Loan
A working capital loan is a short-term loan designed to finance the day-to-day operations of a business, such as payroll, inventory purchases, or other operational expenses. It helps manage cash flow and ensures that the business can continue running smoothly during periods of reduced revenue or increased expenses.
Pros & Cons of Working Capital Loans:
When to Use It: Use a working capital loan when you need immediate funding to cover operational costs, especially during seasonal downturns, slow cash flow periods, or unexpected expenses. It’s suitable for businesses that need short-term financial support and have a reliable plan for repayment.
Learn More About Working Capital LoansMicroloan
A microloan is a small, short-term loan designed to help small businesses and startups with limited access to conventional financing. These loans are often provided by non-profit organizations, government agencies, or microfinance institutions.
Pros & Cons of Microloans for Business:
When to Use It: Use a microloan when your business requires a small amount of capital for startup costs, working capital, or minor equipment purchases, especially if you have limited credit history or collateral. It’s ideal for entrepreneurs and small businesses looking to build credit and gain initial financial support.
Learn More About Microloans for BusinessTrade Finance
Trade finance encompasses a range of financial products and services designed to facilitate international and domestic trade. It includes instruments like letters of credit, export credit, and factoring, which help manage the risks and provide the necessary capital for buying and selling goods and services across borders.
Pros & Cons of Trade Finance:
When to Use It: Use trade finance when engaging in international trade to ensure smooth transactions and manage risks associated with cross-border commerce, such as currency fluctuations, non-payment, or geopolitical issues. It’s particularly useful for businesses looking to expand into new markets or requiring capital to fulfill large orders.
Learn More About Trade FinanceBusiness Line of Credit
A business line of credit is a flexible financing option that provides access to a predetermined amount of funds, which a business can draw from as needed. Interest is only charged on the amount borrowed, not the entire credit limit, and funds can be reused as they are repaid.
Pros & Cons of Business Lines of Credit:
When to Use It: Use a business line of credit when you need flexible, short-term funding to manage cash flow, cover operational expenses, or take advantage of unexpected opportunities. It’s ideal for businesses with fluctuating capital needs and those that can manage regular repayments.
Learn More About Business Lines of CreditBusiness Credit Card
A business credit card provides a revolving line of credit that can be used to cover day-to-day business expenses, similar to a personal credit card. It offers convenience for managing expenses and often includes rewards programs or cashback offers tailored to business needs.
Pros & Cons of Business Credit Cards:
When to Use It: Use a business credit card for short-term financing of daily expenses, such as office supplies, travel, or minor equipment purchases, especially if you can pay off the balance each month to avoid interest charges. It’s also useful for tracking and managing business expenses and building credit.
Learn More About Business Credit CardsCommercial Mortgage
A commercial mortgage is a loan secured by commercial property, such as an office building, warehouse, or retail space, used to purchase, refinance, or redevelop the property.
Pros & Cons of Commercial Mortgages:
When to Use It: Use a commercial mortgage when you need to purchase or refinance commercial real estate and have the financial stability to handle the long-term commitment. It’s suitable for businesses looking to expand their physical presence or invest in property as part of their growth strategy.
Learn More About Commercial MortgagesAsset-Backed Financing
Asset-backed financing means you’re borrowing against the value of your company’s assets. Your equipment, inventory, or property can secure your loan, potentially getting you more capital based on their worth.
The three main types of asset-backed financing are equipment financing, inventory financing, and property-backed loans.

Equipment Financing
Equipment financing involves obtaining a loan or lease to purchase business-related equipment, such as machinery, vehicles, or technology. The equipment itself often serves as collateral for the loan.
Pros & Cons of Equipment Financing:
When to Use It: Use equipment financing when you need to acquire expensive equipment crucial for business operations but prefer to preserve cash flow by spreading the payments over time. It’s ideal for businesses requiring significant machinery, technology, or vehicles to grow and operate efficiently.
Learn More About Equipment FinancingInventory Financing
Inventory financing is a type of short-term loan or line of credit used to purchase inventory. The inventory itself often serves as collateral for the loan, enabling businesses to buy stock without immediately depleting cash reserves.
Pros & Cons of Inventory Financing:
When to Use It: Use inventory financing when you need to purchase large quantities of inventory to prepare for high-demand periods or seasonal sales, and when maintaining cash flow is essential. It’s particularly useful for retail and wholesale businesses that need to keep shelves stocked but prefer to avoid upfront costs.
Learn More About Inventory FinancingProperty-Backed Loans
Property-backed loans use real estate or other valuable property as collateral to secure funding for business needs. Unlike commercial mortgages, which are specifically for purchasing or refinancing commercial property, these loans can be used for a variety of business purposes, such as expansion, working capital, or large purchases.
Pros & Cons of Using Property-Backed Loans for Your Business:
When to Use It: Use property-backed loans when you need significant capital for business growth, operations, or large investments and have valuable property to offer as collateral. This option is suitable for businesses that are confident in their ability to repay the loan and want to leverage existing assets to secure better loan terms.
Learn More About Property-Backed Loans for BusinessRevenue-Based Financing
With revenue-based financing, you borrow against future revenues, paying back a percentage of your sales. This is less about collateral and more about cash flow—a good fit if your sales are solid but unpredictable.
The four main types of revenue-based financing are merchant cash advance, invoice financing (also called accounts receivable financing), invoice factoring, purchase order (PO) financing, and tax credit financing.

Merchant Cash Advance
A merchant cash advance (MCA) provides businesses with a lump sum of cash in exchange for a percentage of future credit card sales. Repayments are typically made daily or weekly based on sales volume.
Pros & Cons of Merchant Cash Advance:
When to Use It: Use a merchant cash advance when you need fast funding for short-term expenses, emergencies, or opportunities and have a consistent volume of credit card sales to manage flexible repayments. It’s suitable for businesses that may not qualify for traditional loans but need immediate working capital.
Learn More About Merchant Cash AdvanceInvoice Financing (aka Accounts Receivable Financing)
Invoice financing, also known as accounts receivable financing, allows businesses to borrow money against their outstanding invoices. The business retains ownership of the invoices and is responsible for collecting payments from customers, repaying the lender as the invoices are paid.
Pros & Cons of Invoice Financing/Account Receivable Financing:
When to Use It: Use invoice financing when you need to improve cash flow while retaining control over your receivables and customer relationships. It’s ideal for businesses with long payment terms looking to unlock cash tied up in unpaid invoices.
Learn More About Invoice Financing / Accounts Receivable FinancingInvoice Factoring
Invoice factoring involves selling your outstanding invoices to a factoring company at a discount. The factoring company typically assumes ownership of the invoices and collects payments directly from your customers.
Pros & Cons of Invoice Factoring:
When to Use It: Use invoice factoring when you need immediate cash to manage operational expenses or growth and prefer to outsource the collections process. It’s suitable for businesses with a high volume of outstanding invoices and those looking to improve cash flow without taking on additional debt.
Learn More About Invoice FactoringPurchase Order (PO) Financing
Purchase order financing provides businesses with funding to pay suppliers for goods needed to fulfill customer orders. The lender pays the supplier directly, and the business repays the lender once the customer pays for the delivered goods.
Pros & Cons of Purchase Order Financing:
When to Use It: Use purchase order financing when you have received large customer orders but lack the cash flow to pay suppliers upfront. It’s ideal for businesses with high-volume or seasonal sales needing to fulfill substantial orders without tying up working capital.
Learn More About Purchase Order FinancingTax Credit Financing
Tax credit financing involves obtaining a loan or line of credit against future tax credits your business expects to receive, such as Scientific Research and Experimental Development (SR&ED) credits or film production tax credits.
Pros & Cons of Tax Credit Financing:
When to Use It: Use tax credit financing when your business has earned or expects to earn significant tax credits and needs immediate capital for ongoing operations or new projects. It’s suitable for businesses in industries like research and development or film production, where tax credits are substantial but disbursements are delayed.
Learn More About Tax Credit FinancingAlternative Financing
This isn’t your traditional bank loan. Alternative financing includes options like debt crowdfunding, peer-to-peer loans, and private loans. It’s a good option when you’re seeking flexibility or when conventional banks aren’t an option.

Crowdfunding (Debt/Loan)
Debt crowdfunding involves raising funds from a large number of individual investors through online platforms. Businesses receive a loan and repay it with interest over time, similar to traditional loans but funded by multiple investors.
Pros & Cons of Debt Crowdfunding for Business:
When to Use It: Use debt crowdfunding when you need to raise funds quickly and may not qualify for traditional bank loans, especially if you can leverage a strong network or community of supporters. It’s suitable for businesses that can attract individual investors with a compelling story and clear repayment plan.
Learn More About Debt/Loan Crowdfunding for BusinessPeer-to-Peer Loans
Peer-to-peer (P2P) loans are obtained through online platforms that connect businesses directly with individual lenders. These loans typically offer a range of terms and interest rates, depending on the business’s creditworthiness and the lender’s criteria.
Pros & Cons of Peer-to-Peer Loans for Business:
When to Use It: Use peer-to-peer loans when you need quick access to capital and have a reasonably good credit score, but prefer a more flexible and accessible option than traditional bank loans. It’s suitable for small to medium-sized businesses looking for alternative financing solutions.
Learn More About Peer-to-Peer Loans for BusinessPrivate Loans
Private loans for business include funds provided by family, friends, and private lenders (such as wealthy individuals) or through private loan brokers. These loans offer more personalized and flexible terms compared to traditional banking systems
Pros & Cons of Private Loans for Business:
When to Use It: Use private loans when you need quick and flexible financing, especially if you do not qualify for traditional bank loans or need customized terms. They are ideal for businesses looking for alternative funding options and willing to manage personal dynamics and potentially higher costs.
Learn More About Private Loans for BusinessPersonal Financing for a Small Business
Sometimes, your best bet is to tap into personal resources. This could mean a personal loan, line of credit, or credit card.

Personal Credit Card for Business
Using a personal credit card for business involves charging business-related expenses to your personal credit card. This can provide quick access to funds but mixes personal and business finances.
Pros & Cons of Using a Personal Credit Card for Your Business:
When to Use It: Use a personal credit card for business when you need immediate funds for small, short-term expenses and have a plan to pay off the balance quickly. It’s suitable for startups or small businesses that might not yet qualify for a business credit card but should be used cautiously to avoid financial complications.
Personal Line of Credit for Business
Using a personal line of credit for business involves tapping into a pre-approved credit line from a bank or financial institution, which you can draw from as needed to cover business expenses. This offers flexibility but combines personal and business finances.
Pros & Cons of Using a Personal Line of Credit for Your Business:
When to Use It: Use a personal line of credit for business when you need flexible, short-term funding for various business expenses and can manage the repayments without straining personal finances. It’s suitable for small businesses or startups that might not have access to a business line of credit but should be used judiciously to avoid financial entanglement.
Personal Loan for Business
A personal loan for business use involves borrowing a lump sum from a bank or financial institution in your name, which is then used to fund business activities. This type of loan is based on your personal creditworthiness rather than your business’s financial status.
Pros & Cons of Using a Personal Loan for Your Business:
When to Use It: Use a personal loan for business when your business is new or lacks a credit history, and you need a lump sum for startup costs, expansion, or other significant expenses. Ensure you can handle the repayments without jeopardizing your personal financial stability.
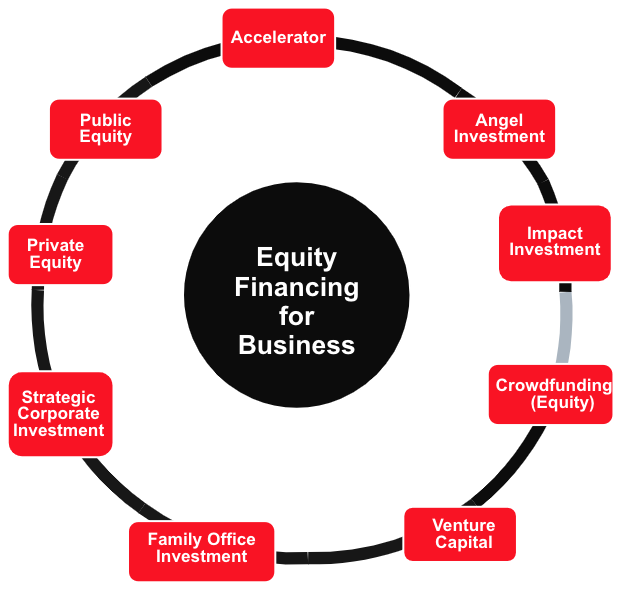
Equity Financing for Your Canadian Business: 9 Ways to Sell a Stake in Your Business

Equity financing invites investors to fund your company in exchange for a piece of ownership. This can be a pivotal step in your business growth, offering capital while avoiding debt.
There are 9 main types of equity financing that entrepreneurs can access in Canada, which we cover below:
Accelerators
A business accelerator that provides equity investment offers startups intensive, short-term support and funding in exchange for an ownership stake. These programs typically include mentorship, networking opportunities, and resources designed to rapidly scale the business.
Pros & Cons of Business Accelerators:
When to Use It: Use a business accelerator for equity investment when you have a validated business model and are ready to scale quickly, seeking both financial investment and expert guidance. It’s ideal for startups looking to grow rapidly and gain access to a robust network of mentors, investors, and industry connections.
Learn More About Business AcceleratorsAngel Investment
Angel investment involves receiving capital from wealthy individuals, known as angel investors, who provide funding in exchange for equity ownership in the business. These investors often bring valuable expertise and mentorship along with their financial support.
Pros & Cons of Angel Investment:
When to Use It: Use angel investment when you need substantial capital to grow your business and can benefit from the investor’s experience and network. It’s suitable for early-stage startups with high growth potential that are willing to exchange equity for both financial support and strategic guidance.
Learn More About Angel InvestmentImpact Investment
Impact investment involves receiving funding from investors who seek both financial returns and positive social or environmental impact. These investors prioritize businesses that address significant societal challenges while maintaining profitability.
Pros & Cons of Impact Investment:
When to Use It: Use impact investment when your business aims to address social or environmental issues and you need capital to scale these efforts while maintaining financial sustainability. It’s ideal for businesses committed to making a positive impact and attracting investors aligned with their mission.
Learn More About Impact InvestmentCrowdfunding (Equity)
Equity crowdfunding involves raising capital from a large number of investors through online platforms in exchange for shares in the company. This method allows businesses to access funds from both accredited and non-accredited investors who gain equity ownership.
Pros & Cons of Equity Crowdfunding:
When to Use It: Use equity crowdfunding when you have a compelling business idea or product and need to raise capital from a broad audience. It’s suitable for startups and growing businesses looking to build a large community of investors and gain substantial funding without relying solely on traditional venture capital.
Venture Capital
Venture capital (VC) involves receiving funding from professional investment firms that specialize in high-risk, high-reward startups. In exchange for significant capital, these firms receive equity stakes in the business and often play an active role in its strategic direction.
Pros & Cons of Venture Capital:
When to Use It: Use venture capital when your business has high growth potential and you need substantial funding to scale rapidly. It’s suitable for startups in technology or innovative sectors that require large capital investments and can benefit from strategic partnerships and expertise from experienced investors.
Learn More About Venture CapitalFamily Office Investment
Family office investment involves securing funding from family offices, which are private wealth management firms that handle the investments and financial affairs of affluent families. These investments can offer flexible terms and substantial capital, often with a long-term perspective.
Pros & Cons of Family Office Investment:
When to Use It: Use family office investment when you need substantial funding and prefer a long-term investment perspective with flexible terms. It’s suitable for businesses that can benefit from strategic support and patient capital, particularly in industries that align with the family office’s interests and values.
Learn More About Family Office InvestmentStrategic Corporate Investment
Strategic corporate investment involves receiving funding from established companies that are looking to invest in startups or smaller businesses that complement their own operations. These investments can include capital, resources, and expertise, often with the intent of forming a strategic partnership.
Pros & Cons of Strategic Corporate Investment:
When to Use It: Use strategic corporate investment when your business can benefit from the resources, expertise, and market position of a larger corporate partner, and when there is a clear alignment of strategic goals. It’s suitable for businesses looking to scale rapidly and willing to collaborate closely with an established company in their industry.
Learn More About Strategic Corporate InvestmentPrivate Equity
Private equity (PE) involves securing investment from private equity firms, which pool funds from institutional and accredited investors to acquire equity stakes in businesses. These firms often focus on established companies with significant growth potential, providing both capital and strategic management support.
Pros & Cons of Private Equity:
When to Use It: Use private equity when your business is established and looking to scale significantly, needing not just capital but also strategic support to optimize operations and drive growth. It’s suitable for businesses ready for transformative growth and willing to collaborate closely with experienced investors.
Learn More About Private EquityPublic Equity
Public equity involves raising capital by issuing shares of the company to the public through a stock exchange in an initial public offering (IPO) or secondary offering. This process allows a business to access a large pool of investors and become publicly traded.
Pros & Cons of Public Equity:
When to Use It: Use public equity when your business is mature, with a solid track record of performance and growth, and when you need significant capital to expand further. It’s suitable for companies ready to handle the complexities of being publicly traded and seeking the benefits of increased capital and market presence.
Learn More About Public Equity